Bettabods quote of the month…….especially for YOU 🙂
Bettabods Quote of the month……
Bettabods quote of the month…….especially for YOU 🙂
We at Bettabods are dedicated to helping you improve yourself, and we love assisting you by giving you something to Motivate you with.
So, with that said, let’s hope our monthly quotes help to do just that!
Are Hunger Hormones Sabotaging your Fat Loss #2
THE LEPTIN SPIRAL
Leptin is stored in and secreted by one’s fat cells. As you gain more fat mass, your leptin levels increase to tell your brain to eat less and burn more calories. Conversely, if you cut down your calories and start to lose body fat, your leptin levels go down, which then sends a signal to your brain to eat more and burn less!
Think of this conundrum as a safety mechanism that regulates energy expenditure as well as food intake. <!–more–>
Based on this information, you would think someone carrying around extra body fat would have more leptin, and thus, fewer desires to overindulge in food. This sounds great in theory, but research has shown that despite an elevation in leptin levels, obese individuals continue to overeat and energy expenditure fails to increase significantly.
This is called leptin-resistance. As someone gains weight, the signal to their brain gets “disrupted” or becomes less “sensitive,” which causes them to continually overeat.
Are Hunger Hormones Sabotaging your Fat Loss #2
THE LEPTIN SPIRAL
Leptin is stored in and secreted by fat cells. As you gain more fat mass, leptin levels increase to tell your brain to eat less and burn more calories. Conversely, if you cut down your calories and start to lose body fat, leptin levels go down, which then sends a signal to your brain to eat more and burn less! Think of this conundrum as a safety mechanism that regulates energy expenditure and food intake.3
Based on this information, you would think someone carrying around extra body fat would have more leptin, and thus, fewer desires to overindulge in food. This sounds great in theory, but research has shown that despite an elevation in leptin levels, obese individuals continue to overeat and energy expenditure fails to increase significantly.
This is called leptin-resistance. As someone gains weight, the signal to their brain can get “disrupted” or become less “sensitive,” which causes them to continually overeat.
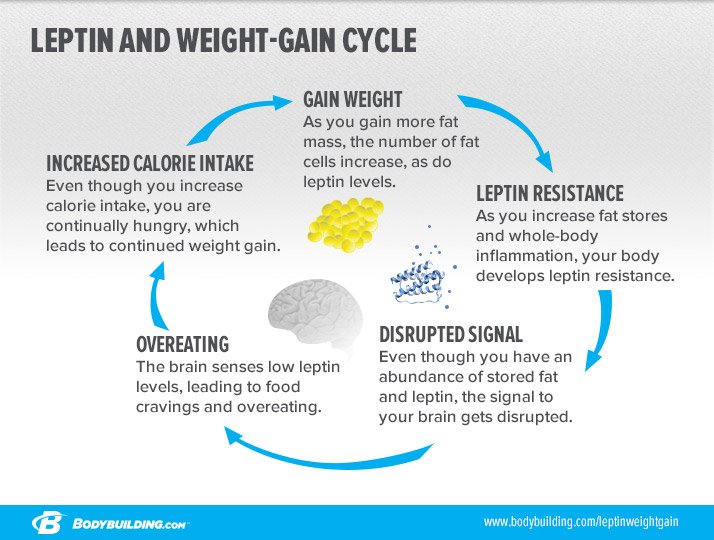
Are Hunger Hormones Sabotaging your Fat Loss #2
THE LEPTIN SPIRAL
Leptin is stored in and secreted by one’s fat cells. As you gain more fat mass, your leptin levels increase to tell your brain to eat less and burn more calories. Conversely, if you cut down your calories and start to lose body fat, your leptin levels go down, which then sends a signal to your brain to eat more and burn less!
Think of this conundrum as a safety mechanism that regulates energy expenditure as well as food intake. <!–more–>
Based on this information, you would think someone carrying around extra body fat would have more leptin, and thus, fewer desires to overindulge in food. This sounds great in theory, but research has shown that despite an elevation in leptin levels, obese individuals continue to overeat and energy expenditure fails to increase significantly.
This is called leptin-resistance. As someone gains weight, the signal to their brain gets “disrupted” or becomes less “sensitive,” which causes them to continually overeat.
Are Hunger Hormones Sabotaging Your Fat Loss #1?
Millions of people go on diets every year, but by the end of the year, most of them have regained any weight lost and find themselves starting back at square one. After all, dieting is no easy feat, and it might even be harder than you think! Your body has an appetite, and if you consistently take in fewer calories than you burn, your body responds by revving up your appetite hormones, making you hungrier.
It’s not uncommon to hear names like insulin, testosterone, estrogen, and cortisol thrown around when talking about hormones that affect body fat. For example, insulin is often cited as a fat-storage hormone and criticized for being a key contributor to weight gain and obesity. While this is oversimplified and not entirely true, there are two hormones that may play a much larger and more direct role in weight gain and weight management: leptin and ghrelin.
These two hunger hormones can directly affect energy balance and play a much bigger role in weight-loss success.1If you want to improve your body composition and be successful with long-term weight management, understanding the role of these two hormones and how you can manipulate them is key!
WHAT IS LEPTIN?
Leptin is considered the master regulator of hunger, and is known as your appetite suppressor. Leptin influences food intake due to its effect on the hypothalamus, a region of the brain that governs many processes and emotions such as hunger, thirst, sleep, and mood.

For example, when you eat a meal, leptin levels increase. This sends a signal to the brain telling your body that it’s full and to put the fork down. However, if an individual is leptin-resistant, or if the leptin pathway isn’t working properly, they may continue to overeat and often have poor control over food intake—in other words, they overeat without even knowing it.2
For these reasons, it’s easy to understand why leptin plays a key role in long-term dietary adherence and success.
Are Hunger Hormones Sabotaging Your Fat Loss #1
LEPTIN AND GHRELIN EXPLAINED?
Millions of people go on diets every year, but by the end of the year, most of them have regained any weight lost and find themselves starting back at square one. After all, dieting is no easy feat, and it might even be harder than you think! Your body has an appetite, and if you consistently take in fewer calories than you burn, your body responds by revving up your appetite hormones, making you hungrier.
It’s not uncommon to hear names like insulin, testosterone, estrogen, and cortisol thrown around when talking about hormones that affect body fat. For example, insulin is often cited as a fat-storage hormone and criticized for being a key contributor to weight gain and obesity. While this is oversimplified and not entirely true, there are two hormones that may play a much larger and more direct role in weight gain and weight management: leptin and ghrelin.
These two hunger hormones can directly affect energy balance and play a much bigger role in weight-loss success.1If you want to improve your body composition and be successful with long-term weight management, understanding the role of these two hormones and how you can manipulate them is key!
WHAT IS LEPTIN?
Leptin is considered the master regulator of hunger, and is known as your appetite suppressor. Leptin influences food intake due to its effect on the hypothalamus, a region of the brain that governs many processes and emotions such as hunger, thirst, sleep, and mood.
LEPTIN INFLUENCES FOOD INTAKE DUE TO ITS EFFECT ON THE HYPOTHALAMUS, A REGION OF THE BRAIN THAT GOVERNS MANY PROCESSES AND EMOTIONS SUCH AS HUNGER, THIRST, SLEEP, AND MOOD.
For example, when you eat a meal, leptin levels increase. This sends a signal to the brain telling your body that it’s full and to put the fork down. However, if an individual is leptin-resistant, or if the leptin pathway isn’t working properly, they may continue to overeat and often have poor control over food intake—in other words, they overeat without even knowing it.2
For these reasons, it’s easy to understand why leptin plays a key role in long-term dietary adherence and success.
Are Hunger Hormones Sabotaging Your Fat Loss #1?
Millions of people go on diets every year, but by the end of the year, most of them have regained any weight lost and find themselves starting back at square one. After all, dieting is no easy feat, and it might even be harder than you think! Your body has an appetite, and if you consistently take in fewer calories than you burn, your body responds by revving up your appetite hormones, making you hungrier.
It’s not uncommon to hear names like insulin, testosterone, estrogen, and cortisol thrown around when talking about hormones that affect body fat. For example, insulin is often cited as a fat-storage hormone and criticized for being a key contributor to weight gain and obesity. While this is oversimplified and not entirely true, there are two hormones that may play a much larger and more direct role in weight gain and weight management: leptin and ghrelin.
These two hunger hormones can directly affect energy balance and play a much bigger role in weight-loss success.1If you want to improve your body composition and be successful with long-term weight management, understanding the role of these two hormones and how you can manipulate them is key!
WHAT IS LEPTIN?
Leptin is considered the master regulator of hunger, and is known as your appetite suppressor. Leptin influences food intake due to its effect on the hypothalamus, a region of the brain that governs many processes and emotions such as hunger, thirst, sleep, and mood.

For example, when you eat a meal, leptin levels increase. This sends a signal to the brain telling your body that it’s full and to put the fork down. However, if an individual is leptin-resistant, or if the leptin pathway isn’t working properly, they may continue to overeat and often have poor control over food intake—in other words, they overeat without even knowing it.2
For these reasons, it’s easy to understand why leptin plays a key role in long-term dietary adherence and success.
Are Hunger Hormones Sabotaging Your Fat Loss?
Millions of people go on diets every year, but by the end of the year, most of them have regained any weight lost and find themselves starting back at square one. After all, dieting is no easy feat, and it might even be harder than you think! Your body has an appetite, and if you consistently take in fewer calories than you burn, your body responds by revving up your appetite hormones, making you hungrier.
It’s not uncommon to hear names like insulin, testosterone, estrogen, and cortisol thrown around when talking about hormones that affect body fat. For example, insulin is often cited as a fat-storage hormone and criticized for being a key contributor to weight gain and obesity. While this is oversimplified and not entirely true, there are two hormones that may play a much larger and more direct role in weight gain and weight management: leptin and ghrelin.
These two hunger hormones can directly affect energy balance and play a much bigger role in weight-loss success.1If you want to improve your body composition and be successful with long-term weight management, understanding the role of these two hormones and how you can manipulate them is key!
WHAT IS LEPTIN?
Leptin is considered the master regulator of hunger, and is known as your appetite suppressor. Leptin influences food intake due to its effect on the hypothalamus, a region of the brain that governs many processes and emotions such as hunger, thirst, sleep, and mood.

For example, when you eat a meal, leptin levels increase. This sends a signal to the brain telling your body that it’s full and to put the fork down. However, if an individual is leptin-resistant, or if the leptin pathway isn’t working properly, they may continue to overeat and often have poor control over food intake—in other words, they overeat without even knowing it.2
For these reasons, it’s easy to understand why leptin plays a key role in long-term dietary adherence and success.
Are Hunger Hormones Sabotaging Your Fat Loss #1
LEPTIN AND GHRELIN EXPLAINED?
Millions of people go on diets every year, but by the end of the year, most of them have regained any weight lost and find themselves starting back at square one. After all, dieting is no easy feat, and it might even be harder than you think! Your body has an appetite, and if you consistently take in fewer calories than you burn, your body responds by revving up your appetite hormones, making you hungrier.
It’s not uncommon to hear names like insulin, testosterone, estrogen, and cortisol thrown around when talking about hormones that affect body fat. For example, insulin is often cited as a fat-storage hormone and criticized for being a key contributor to weight gain and obesity. While this is oversimplified and not entirely true, there are two hormones that may play a much larger and more direct role in weight gain and weight management: leptin and ghrelin.
These two hunger hormones can directly affect energy balance and play a much bigger role in weight-loss success.1If you want to improve your body composition and be successful with long-term weight management, understanding the role of these two hormones and how you can manipulate them is key!
WHAT IS LEPTIN?
Leptin is considered the master regulator of hunger, and is known as your appetite suppressor. Leptin influences food intake due to its effect on the hypothalamus, a region of the brain that governs many processes and emotions such as hunger, thirst, sleep, and mood.
LEPTIN INFLUENCES FOOD INTAKE DUE TO ITS EFFECT ON THE HYPOTHALAMUS, A REGION OF THE BRAIN THAT GOVERNS MANY PROCESSES AND EMOTIONS SUCH AS HUNGER, THIRST, SLEEP, AND MOOD.
For example, when you eat a meal, leptin levels increase. This sends a signal to the brain telling your body that it’s full and to put the fork down. However, if an individual is leptin-resistant, or if the leptin pathway isn’t working properly, they may continue to overeat and often have poor control over food intake—in other words, they overeat without even knowing it.2
For these reasons, it’s easy to understand why leptin plays a key role in long-term dietary adherence and success.
